 Bipolar disorders is a complex and often misunderstood medical condition, marked by dramatic shifts in mood, energy, and behavior. Characterized by alternating periods of mania and depression, it profoundly impacts daily functioning and interpersonal relationships.
Bipolar disorders is a complex and often misunderstood medical condition, marked by dramatic shifts in mood, energy, and behavior. Characterized by alternating periods of mania and depression, it profoundly impacts daily functioning and interpersonal relationships.
This article aims to unravel the complexities of bipolar disorder. I will be debunking common myths and offering insights into its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
By addressing prevalent misconceptions and providing a comprehensive overview of treatment options, I hope to foster a deeper understanding of this condition. Plus highlight the importance of accurate diagnosis and effective management.
I’m sharing about this topic because I’m a bestselling wellness author and leading Behavioral Change Expert. I am committed to helping people to live their best lives – no matter their challenges.
Whether you are seeking to learn more for personal reasons or to support someone you care about, this guide will provide valuable information on navigating the challenges of bipolar disorder.
Key Takeaways about Bipolar Disorder
- Bipolar disorder involves extreme mood swings, impacting daily life, relationships, and physical health, with symptoms including manic and depressive episodes.
- Contrary to common myths, bipolar disorder is not rare, mania is not always enjoyable, and children can be diagnosed with this mental disorder.
- Effective bipolar disorder treatment requires a combination of medications, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes, alongside ongoing support and management to prevent relapse and maintain stability.
The Basics About Bipolar Disorder
What is Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar disorder, sometimes known as manic-depressive illness, is a mental health condition characterized by significant mood changes, energy levels, and the ability to function in daily life, by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). Most people experience mood swings as periods of intensely elevated moods (manic episodes) and periods of deep sadness or hopelessness (depressive episodes). The disorder can affect anyone. It typically emerges in late adolescence or early adulthood. And it can have profound impacts on personal relationships, work, and overall quality of life.
Manic Episodes
A manic episode is defined by abnormally elevated or irritable mood, heightened energy, and often risky or impulsive behaviors.
Symptoms of mania can include:
- Excessive euphoria or irritability
- Decreased need for sleep
- Rapid speech, racing thoughts, difficulty focusing
- Grandiose ideas or inflated self-esteem
- Impulsive or reckless behaviors, such as spending sprees or unwise investments
- Hyperactivity and increased goal-directed activities
These manic episodes can be severe enough to require hospitalization to prevent harm to oneself or others. And they significantly impair a person’s ability to function in everyday activities.
Depressive Symptoms
A depressive episode in bipolar disorder are characterized by prolonged periods of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in nearly all activities. Symptoms of depression can include at least one episode of:
- Persistent feelings of sadness or emptiness
- Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed
- Significant weight loss or gain, or changes in appetite
- Insomnia or excessive sleeping
- Fatigue or loss of energy
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Thoughts of death or suicide
These mania and depression symptoms can be debilitating. They can impact a person’s ability to perform at work or school, maintain relationships, and manage day-to-day tasks.
Types of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is classified into several types based on the pattern and severity of symptoms:
- Bipolar I Disorder: This type is characterized by at least one manic episode lasting at least seven days. Or by manic symptoms severe enough to require immediate hospitalization. Depressive episodes typically occur as well and last for at least two weeks.
- Bipolar II Disorder: This type involves at least one hypomanic episode (a less severe form of mania) and at least one major depressive episode. Hypomanic episodes do not usually cause significant impairment in daily functioning.
- Cyclothymic Disorder: This type is defined by numerous periods of hypomanic symptoms and periods of depressive symptoms lasting for at least two years (one year in children and adolescents). However, the symptoms do not meet the diagnostic criteria for a hypomanic or depressive episode.
- Other Specified and Unspecified Bipolar and Related Disorders: These categories include bipolar disorder symptoms that do not match the specific criteria for the above types. But it still involves significant mood disturbances.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Diagnosing bipolar disorder involves a thorough evaluation by a mental health professional. They will consider a person’s medical history, symptoms, and family history. Key symptoms to be identified include:
- Experiencing mania, hypomanic, or depressive episodes
- Significant mood episodes and changes in energy and activity levels
- Impaired functioning in daily life
To meet diagnostic criteria for bipolar disorder, the clinician will use criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). This process often includes ruling out other mental health conditions, such as major depressive disorder or borderline personality disorder, and assessing for co-occurring conditions like substance use disorder, post traumatic stress disorder or other anxiety disorders.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing bipolar disorder effectively and improving quality of life. Treatment typically involves a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle adjustments to help stabilize mood swings and reduce the impact of symptoms on daily life.
Common Myths About Bipolar Disorder
 Bipolar disorder is a widely misunderstood condition, often surrounded by myths that can lead to stigma and misinformation. Dispelling these myths is crucial for fostering a more empathetic and accurate understanding of the disorder. Here are three common misconceptions about bipolar disorder:
Bipolar disorder is a widely misunderstood condition, often surrounded by myths that can lead to stigma and misinformation. Dispelling these myths is crucial for fostering a more empathetic and accurate understanding of the disorder. Here are three common misconceptions about bipolar disorder:
Myth #1: Bipolar Disorder is Rare.
Fact: Bipolar disorder is not rare. It affects millions of people worldwide, with an estimated 46 million individuals, or about 0.53% of the global population, living with the condition. In the United States alone, approximately 2.8% of adults experience bipolar disorder annually. The misconception that bipolar disorder is uncommon contributes to the stigma and lack of awareness about the condition. Recognizing its prevalence can help promote better understanding and support for those affected.
Myth #2: Mania is Always Enjoyable.
Fact: While some individuals may experience heightened energy and euphoria during manic episodes, these periods are often accompanied by significant distress and risky behaviors. Mania can include irritability, agitation, impulsivity, and poor decision-making. These symptoms can lead to severe consequences such as financial problems, relationship issues, and even hospitalization. The belief that mania is always pleasurable overlooks the potential for dangerous and harmful behaviors that often require medical intervention and support.
Myth #3: Children Cannot Have Bipolar Disorder.
Fact: Bipolar disorder can indeed be diagnosed in children and adolescents, though their symptoms may differ from those seen in adults. In young people, bipolar disorder often presents as severe mood swings, irritability, and behavioral issues. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing the disorder effectively and helping young individuals lead healthy, productive lives. Recognizing that children can have bipolar disorder underscores the importance of early mental health screenings and appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Bipolar Disorder
Effective treatment to help manage bipolar disorder typically involves a combination of medications, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. This multifaceted approach aims to stabilize mood swings, reduce the frequency and severity of episodes, and improve overall functioning and quality of life.
Medications for Mental Health Conditions like Bipolar Disorder
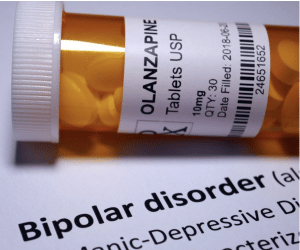 Medications play a crucial role in managing bipolar disorder. The primary types of medications used include mood stabilizers, antipsychotic medications, and antidepressants.
Medications play a crucial role in managing bipolar disorder. The primary types of medications used include mood stabilizers, antipsychotic medications, and antidepressants.
- Mood Stabilizers: These are the cornerstone of bipolar disorder treatment. Lithium, valproic acid (Depakote), and lamotrigine (Lamictal) are commonly prescribed to help control manic and hypomanic episodes, erratic behavior and prevent future mood swings.
- Antipsychotic Medications: For individuals who do not respond adequately to mood stabilizers alone, antipsychotic medications like olanzapine (Zyprexa), risperidone (Risperdal), and quetiapine (Seroquel) may be used. These medications can help manage symptoms of mania and, in some cases, depression.
- Antidepressants: These may be used to treat depressive episodes in bipolar disorder, but they are usually prescribed in conjunction with a mood stabilizer to prevent triggering a manic episode. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are common choices.
- Other Medications: Anti-anxiety medications and sleep aids might be prescribed to address co-occurring symptoms like anxiety and insomnia.
Finding the right medication or combination of medications can take time and often requires close monitoring by a healthcare provider to manage side effects and adjust dosages.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, is a vital component of treatment for bipolar disorder. It helps individuals understand their condition, develop coping strategies, and address issues that contribute to mood swings. Several types of psychotherapy have proven effective:
- Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to mood episodes. It also teaches practical skills for managing stress and preventing relapse.
- Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT): Interpersonal therapy focuses on stabilizing daily routines and improving interpersonal relationships. Regularizing daily activities, such as sleep and meal times, can help stabilize mood swings.
- Psychoeducation: Educating individuals and their families about bipolar disorder is crucial. Understanding the condition, recognizing early signs of mood episodes, and knowing when to seek help can empower individuals to manage their symptoms effectively.
- Family-Focused Therapy: This type of therapy involves family members in the treatment process, improving communication, reducing stress, and providing support for managing the disorder.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Help Strategies to Cope with Mood Swings
 Lifestyle changes and self-help strategies are essential for managing bipolar disorder and maintaining stability. Here are some effective approaches:
Lifestyle changes and self-help strategies are essential for managing bipolar disorder and maintaining stability. Here are some effective approaches:
- Regular Routine: Establishing a consistent daily routine, including regular sleep patterns, meals, and exercise, can help stabilize mood swings.
- Healthy Sleep Habits: Prioritizing good sleep hygiene is critical. Aim for a regular sleep schedule, create a calming bedtime routine, and avoid caffeine or stimulating activities before bed.
- Balanced Diet and Exercise: Eating a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can improve overall health and help manage stress. Exercise is particularly beneficial for reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and prevent mood episodes.
- Avoiding Substance Use: Alcohol and recreational drugs can exacerbate bipolar symptoms and interact negatively with medications. Avoiding substance abuse is crucial for maintaining emotional stability.
- Support Network: Building a strong support network of friends, family, and support groups can provide emotional support and practical assistance during challenging times.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Keeping track of mood changes, sleep patterns, and triggers in a mood diary can help individuals and their healthcare providers identify early signs of mood episodes and adjust treatment as needed.
By combining medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes, people with bipolar disorder can achieve better control over their symptoms, reduce the impact of mood swings, and improve their overall quality of life.
The Importance of Ongoing Treatment
The importance of ongoing treatment for bipolar disorder cannot be overstated, as it is crucial for preventing relapse and effectively managing symptoms. Continuous treatment, at a Massachusetts rehab center, helps stabilize mood fluctuations and reduces the risk of recurring manic or depressive episodes, which can become more frequent and severe if left untreated.
Regular medication adherence, psychotherapy sessions, and lifestyle modifications are vital components of a long-term treatment plan that not only mitigates symptoms but also enhances overall functioning and quality of life. Consistent monitoring by healthcare professionals ensures that the treatment remains effective and adjustments are made as needed.
By maintaining a committed approach to treatment, people with bipolar disorder can achieve better control over their condition, leading to improved stability and well-being.
Impact of Bipolar Disorder on Daily Life
Bipolar disorder significantly affects various aspects of daily life, influencing work productivity, personal relationships, and physical health. Understanding these impacts can help in developing effective strategies to manage the disorder and improve quality of life.
Work and Productivity
People with bipolar disorder often face challenges in maintaining consistent work performance and coping with workplace stress. The mood swings associated with the disorder can lead to periods of high productivity during manic phases, followed by severe drops in performance during depressive episodes.
This inconsistency can result in difficulties with job retention, career advancement, and overall job satisfaction. Creating a supportive work environment, including flexible work hours and regular breaks, can help people with bipolar disorder manage their symptoms and maintain productivity.
Relationships
The mood fluctuations inherent in bipolar disorder can strain personal relationships, causing misunderstandings and conflicts with family, friends, and partners. Manic episodes may lead to impulsive and sometimes harmful behaviors, while depressive episodes can result in withdrawal and lack of communication. These dynamics can create stress and tension in relationships, making it essential for loved ones to understand the disorder and provide compassionate support.
Open communication, patience, and involvement in therapy can help strengthen relationships and provide a stable support system for those affected by bipolar disorder.
Physical Health
Bipolar disorder can have a profound impact on physical health. Irregular sleep patterns, common during both manic and depressive episodes, can lead to chronic sleep disturbances, which in turn exacerbate mood symptoms. Additionally, people with bipolar disorder are at higher risk for co-occurring conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity, partly due to the side effects of medications and lifestyle factors.
Managing these physical health issues requires a comprehensive treatment plan that includes regular medical check-ups, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and healthy sleep habits. Addressing both the mental and physical aspects of the disorder is crucial for overall well-being.
In summary, the impact of bipolar disorder on daily life is multifaceted, affecting work, relationships, and physical health. With proper treatment and support, individuals can manage these challenges and lead fulfilling lives.
How To Support People with Bipolar Disorder and Other Mental Health Conditions
 Supporting a loved one with bipolar disorder involves recognizing symptoms, offering practical and emotional support, and working to reduce the stigma associated with the condition. By being informed and compassionate, you can significantly contribute to their well-being and stability.
Supporting a loved one with bipolar disorder involves recognizing symptoms, offering practical and emotional support, and working to reduce the stigma associated with the condition. By being informed and compassionate, you can significantly contribute to their well-being and stability.
Recognizing Symptoms
Understanding and recognizing the symptoms of bipolar disorder is crucial for providing effective support. Manic episodes are characterized by elevated energy levels, decreased need for sleep, increased talkativeness, and impulsive behaviors. Depressive episodes, on the other hand, involve persistent sadness, fatigue, loss of interest in activities, and feelings of hopelessness.
Early identification of these symptoms can help in taking timely action to manage the mood swings and prevent them from escalating. Keeping a watchful eye on changes in mood, behavior, and daily routines can facilitate early intervention and better management of the disorder.
Offering Support
Offering support to a loved one with bipolar disorder involves being an empathetic listener and providing nonjudgmental emotional support. Encourage open communication, allowing them to express their feelings and experiences without fear of criticism. Help them with daily tasks when they are experiencing depressive episodes, as this can alleviate some of their burden.
Accompanying them to medical appointments and therapy sessions can also provide a sense of reassurance and accountability. Additionally, educating yourself about bipolar disorder and its treatment options can enable you to offer informed support and advice.
Reducing Stigma
Reducing the stigma associated with bipolar disorder is essential for fostering an environment of understanding and acceptance. Challenge misconceptions and stereotypes about the disorder by sharing accurate information and personal experiences. Use respectful language that emphasizes the person rather than their condition, such as “a person with bipolar disorder” instead of “a bipolar person.”
Supporting mental health advocacy groups and encouraging others to learn about mental health issues can also help to create a more compassionate and educated community. By advocating for awareness and understanding, you can contribute to a more supportive and stigma-free environment for your loved one.
In conclusion, supporting a loved one with bipolar disorder requires recognizing symptoms, providing emotional and practical support, and actively working to reduce stigma. Your understanding and compassion can make a significant difference in their journey towards stability and well-being.
How to Manage Bipolar Disorder and Similar Symptoms
Understanding and supporting people with bipolar disorder is crucial for fostering empathy and effective management of the condition. By debunking myths, recognizing the significant impact on daily life, and emphasizing the importance of ongoing treatment, we can promote a more compassionate and informed approach.
Effective support involves recognizing symptoms, offering practical and emotional support, and reducing stigma. With proper treatment and a supportive environment, people with bipolar disorder can achieve stability and lead fulfilling lives, contributing to a more inclusive and understanding society for all affected by mental health conditions.
Learn to Eat Healthier
Explore my bestselling and nutritionist recommended online program: The Stop Emotional Eating Course.
P.S. Before you zip off to your next Internet pit stop, check out these 2 game changers below - that could dramatically upscale your life.
1. Check Out My Book On Enjoying A Well-Lived Life: It’s called "Your To Die For Life: How to Maximize Joy and Minimize Regret Before Your Time Runs Out." Think of it as your life’s manual to cranking up the volume on joy, meaning, and connection. Learn more here.
2. Life Review Therapy - What if you could get a clear picture of where you are versus where you want to be, and find out exactly why you’re not there yet? That’s what Life Review Therapy is all about.. If you’re serious about transforming your life, let’s talk. Learn more HERE.
Think happier. Think calmer.
Think about subscribing for free weekly tools here.
No SPAM, ever! Read the Privacy Policy for more information.
One last step!
Please go to your inbox and click the confirmation link we just emailed you so you can start to get your free weekly NotSalmon Happiness Tools! Plus, you’ll immediately receive a chunklette of Karen’s bestselling Bounce Back Book!

 Bipolar disorders is a complex and often misunderstood medical condition, marked by dramatic shifts in mood, energy, and behavior. Characterized by alternating periods of mania and depression, it profoundly impacts daily functioning and interpersonal relationships.
Bipolar disorders is a complex and often misunderstood medical condition, marked by dramatic shifts in mood, energy, and behavior. Characterized by alternating periods of mania and depression, it profoundly impacts daily functioning and interpersonal relationships. Bipolar disorder is a widely misunderstood condition, often surrounded by myths that can lead to stigma and misinformation. Dispelling these myths is crucial for fostering a more empathetic and accurate understanding of the disorder. Here are three common misconceptions about bipolar disorder:
Bipolar disorder is a widely misunderstood condition, often surrounded by myths that can lead to stigma and misinformation. Dispelling these myths is crucial for fostering a more empathetic and accurate understanding of the disorder. Here are three common misconceptions about bipolar disorder: Medications play a crucial role in managing bipolar disorder. The primary types of medications used include mood stabilizers, antipsychotic medications, and antidepressants.
Medications play a crucial role in managing bipolar disorder. The primary types of medications used include mood stabilizers, antipsychotic medications, and antidepressants. Lifestyle changes and self-help strategies are essential for managing bipolar disorder and maintaining stability. Here are some effective approaches:
Lifestyle changes and self-help strategies are essential for managing bipolar disorder and maintaining stability. Here are some effective approaches: Supporting a loved one with bipolar disorder involves recognizing symptoms, offering practical and emotional support, and working to reduce the stigma associated with the condition. By being informed and compassionate, you can significantly contribute to their well-being and stability.
Supporting a loved one with bipolar disorder involves recognizing symptoms, offering practical and emotional support, and working to reduce the stigma associated with the condition. By being informed and compassionate, you can significantly contribute to their well-being and stability.